Windows ReadyBoost allows user to make use of relatively cheap USB flash drive, memory stick or memory card as extra additional disk-based cache memory to speed up and boost performance of Windows Vista and Windows 7 operating system, and improve system responsiveness. Windows uses ReadyBoost memory to supplement the existing virtual memory, which is stored on slow hard disk drive.
In order to be able to be used as the virtual memory caching storage medium by ReadyBoost, the removable media will need to meet the following hardware and speed requirements:
- The capacity of the removable media is at least 256 MB (or 250 MB after formatting).
- The flash memory devices must be capable of 2.5MB/sec throughput for 4K random reads spread uniformly across the entire device.
- The flash memory devices must also be capable of 1.75MB/sec throughput for 512K random writes spread uniformly across the device.
- The removable media device should have an access time of 1ms or less.
- The flash media must have at least 235 MB of free storage psace.
- Formatted as NTFS or FAT32 filesystem, both can make use a maximum of 4 GB of flash memory, which is the ReadyBoost limit, and in FAT32 case, the ReadyBoost.sfcache file size is also limited by FAT32 filesystem to 4GB.
- ReadyBoost supports one flash device at any one time as of currently.
Of course, ReadyBoost won’t outperform adding additional physical RAM memory, but it’s a good alternative for users with existing or spare USB flash drive to gain some free speed boost. Here’s how to turn on and enable ReadyBoost on Windows Vista and Windows 7 system.
- Insert the USB 2.0 flash drive (memory stick, thumbdrive, pendrive, key drive and etc) into USB port, or a memory card (SD, SDHC MMC, CF, MS, xD and etc) into a card reader.
- On AutoPlay pop-up window, select Speed up my system using Windows ReadyBoost.
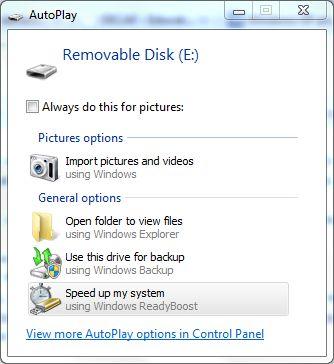
Alternatively, if there is no AutoPlay dialog, right click on the removable disk drive in Windows Explorer, and select Properties. Then, go to ReadyBoost tab.
- Select Dedicate this device to ReadyBoost option to use entire flash memory space on the device as ReadyBoost virtual memory, up to a maximum of 4GB.
Select Use this device and then specify to space to reserve for system speed using the slider bar or specify the value in MB in the text box below the option.
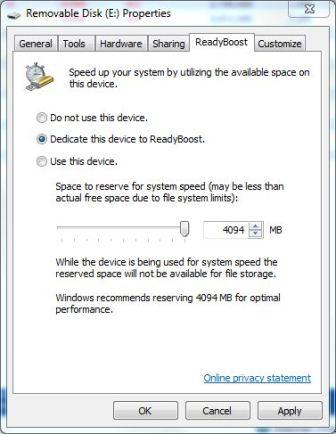
- Click OK.
ReadyBoost will start using the device instantly. If the USB flash drive or memory card reader has LED indicator, the light will be flashing continuously, even without read or write operation initiated by user.
For subpar flash memory devices, there is hack to force enable ReadyBoost on device that does not meet requirements. If the removable disk media should have passed the speed requirement check, here’s a workaround to clean up ReadyBoost registry keys to start afresh.
Recent Posts
- Able2Extract Professional 11 Review – A Powerful PDF Tool
- How to Install Windows 10 & Windows 8.1 with Local Account (Bypass Microsoft Account Sign In)
- How to Upgrade CentOS/Red Hat/Fedora Linux Kernel (cPanel WHM)
- How to Install Popcorn Time Movies & TV Shows Streaming App on iOS (iPhone & iPad) With No Jailbreak
- Stream & Watch Free Torrent Movies & TV Series on iOS with Movie Box (No Jailbreak)
 Tip and Trick
Tip and Trick
- How To Download HBO Shows On iPhone, iPad Through Apple TV App
- Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 19025 (20H1) for PC Official Available for Insiders in Fast Ring – Here’s What’s News, Fixes, and Enhancement Changelog
- Kaspersky Total Security 2020 Free Download With License Serial Key
- Steganos Privacy Suite 19 Free Download With Genuine License Key
- Zemana AntiMalware Premium Free Download For Limited Time