Windows Virtual PC and Windows XP Mode (XPM, previously known as Virtual Windows XP or VXP) are two new optional components for specific editions of Windows 7 operating system. Windows Virtual PC is the Virtual PC (VPC) for Windows 7 which allows user to run virtual machines for virtualization with additional features, such as Windows XP Mode, which allows user to access and run applications installed in virtualized instance of Windows XP on Windows 7 host desktop for backward compatibility.
With much improved functionalities, Windows Virtual PC and Windows XP Mode must be tempting many Windows 7 users. However, Windows Virtual PC system requirements (Windows XP Mode is actually just a virtual machine running pre-activated Windows XP which utilizes features of Windows Virtual PC) have been much different from Virtual PC 2007 SP1. The most significant change is the requirement of hardware-assisted virtualization technology (VT) support.
Update: Microsoft has release KB977206 which hacks Windows Virtual PC and Windows XP Mode to run without hardware-assisted virtualization.
Hardware virtualization technology or VT is built-in natively by CPU processors. In Intel chip, the VT is called Intel VT, while AMD calls it AMD-V. The VT capability in the processor on the computer is built onto the the tiny piece of chip, and cannot be added or removed using any manual process. And even if the CPU features VT, it must be enabled in BIOS.
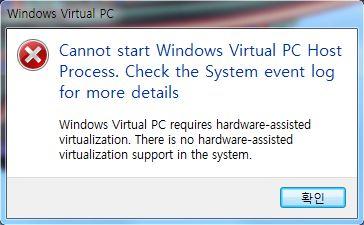
Most newer CPU includes VT operation by default. However, some older or even current processors available for purchase for DIY or operating on OEM computer may not support VT. When there is no VT support, Windows Virtual PC may fail to install or cannot be powered up and started virtual machine with following error message:
Cannot Windows Virtual PC host process. Check the System event log for more details.
Windows Virtual PC requires hardware-assisted virtualization. There is no hardware-assisted virtualization support in the system.
Instead of browsing through the long list of Intel processor’s feature list or AMD CPU’s feature to confirm the existence or non-existence of VT support, there is an easier way to quickly determine whether there is hardware virtualization system on the system. That’s by using SecurAble, a small utility that display status of CPU maximum bit length, DEP and virtualization support.
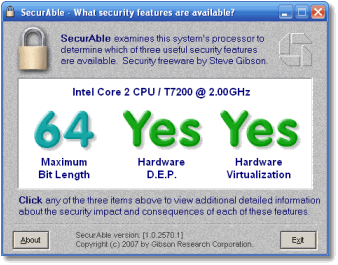
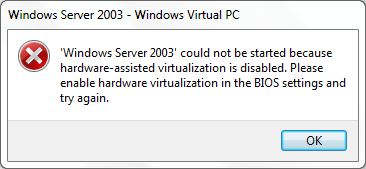
Just download and run SecurAble (no installation required). The status of hardware virtualization feature on the CPU processor is quickly display on screen. If it’s a “Yes” or “Locked On”, the Windows Virtual PC and Windows XP Mode can be used properly. If it’s a “No”, then you’re out of luck. However, there is another possibility that the result may display as “Locked Off”, which means the VT support is currently disabled by BIOS. In this case, just restart the computer and access the BIOS configuration to enable and turn on hardware virtualization support. Else you face the following error when try to launch Windows Virtual PC 7 virtual machine.
Virtual machine could not be started because hardware-assisted virtualization is disabled. Please enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS settings and try again.
Another tool that can be used to detect hardware virtualization support on CPU is HAV Tool from Microsoft.
Recent Posts
- Able2Extract Professional 11 Review – A Powerful PDF Tool
- How to Install Windows 10 & Windows 8.1 with Local Account (Bypass Microsoft Account Sign In)
- How to Upgrade CentOS/Red Hat/Fedora Linux Kernel (cPanel WHM)
- How to Install Popcorn Time Movies & TV Shows Streaming App on iOS (iPhone & iPad) With No Jailbreak
- Stream & Watch Free Torrent Movies & TV Series on iOS with Movie Box (No Jailbreak)
 Tip and Trick
Tip and Trick
- How To Download HBO Shows On iPhone, iPad Through Apple TV App
- Windows 10 Insider Preview Build 19025 (20H1) for PC Official Available for Insiders in Fast Ring – Here’s What’s News, Fixes, and Enhancement Changelog
- Kaspersky Total Security 2020 Free Download With License Serial Key
- Steganos Privacy Suite 19 Free Download With Genuine License Key
- Zemana AntiMalware Premium Free Download For Limited Time